Information about Brazil
- Nov
- 27
- Category: Life in Brazil, Why Brazil
General Information¬† Brazil is the largest country in South America, located in the central and eastern parts of the continent. The length of the land border is about 16 thousand kilometers., Eastern border is over 7.4 thousand km; country is surrounded by theAtlantic Ocean.Brazil‚Äôs area is 8.5 million square km. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, ¬†population ofBrazil in 1999 was 171,853 thousand citizens. Currently,Brazil is FederalRepublic,¬† divided into 23 states, three territories and the Federal District. Capital of Brazil is Brasilia. Currency ¬†– Brazilian real. Official language – Portuguese. Brazilian economy¬† The¬† main feature of Brazilian economy is large and well-developed agriculture, ¬†mining and machine building. Brazil’s economy exceeds the economies of all other South American countries and has been developing rapidly. Since 2003 Brazil has improved its macroeconomic stability, creating currency reserves and reducing debt.
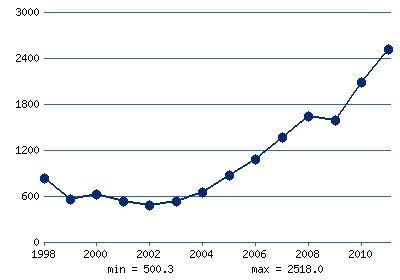
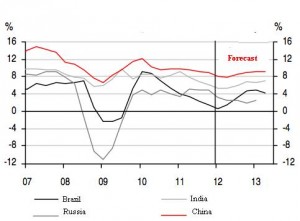
Brazil is one of the key countries in the developing world. In terms of GDP, it is the first in Latin America, in terms of industrial production it is among the top ten countries in the world. The share of industry in GDP – 26.4%, ¬†agriculture – 6.1%. The industry employs 14% of the labor force.. Natural resources of Brazil. Brazil has large deposits of minerals: iron (100 billion tons), manganese (100 million tons), uranium (256 tons), coal (21 billion tons), oil, etc. The most important are iron and manganese ore. From produced more than 200 million tons of iron ore per year, about 80% is exported. ¬†Brazil is one of the largest world suppliers of strategic raw materials: tungsten, niobium, zirconium, mica and other.¬† Country is among the top ten world producers of steel (25 million tons). The largest plants are located in the states of Minas Geral and Sao Paulo. Energy and oil reserves Brazil oil reserves can supply only half of fuel requirement and country have to import the rest. The annual demand for oil is 75 million tons. ¬†There are deposits of coal, but coal is of poor quality and ¬†production volume is about 5 million tonnes per year. Up to 90% of the country’s electricity is produced on hydro power stations and Brazil has a huge hydropower potential. ¬†There ¬†also some uses of alternative sources: ethanol (most of cars run ethanol), wood, coal, nuclear energy (one power plant). Agriculture in Brazil Brazilian agriculture employs 20% of country’s labor force. Brazil is the third largest ¬†world exporter of agricultural products. The major business in agriculture is crop ( wheat, corn and rice)¬† production (60% of total production on ¬†80% of all cultivated land areas). Brazil is traditional manufacturer and exporter of a number of agricultural products: coffee, sugar cane, soybeans, corn, cocoa, bananas, cotton, and cattle. Crisis in Brazil¬† After rapid growth in 2007 and 2008, Brazil experienced two quarters of recession in 2008, ¬†as global demand for Brazilian goods decreased.¬† However,Brazil was one of the first developing countries where recovery has started. ¬†In 2010 consumption and investor confidence were restored, and GDP growth turned positive. ¬†Currently, strong growth in Brazil and relatively high interest rates made ¬†economy of the country attractive to foreign investors. Large capital inflows in 2010 contributed to the rapid growth ¬† of Brazilian real and forced government to raise taxes on some foreign investments. Another positive for Brazil economy fact is huge economic boom in China, which increased demand¬† for all kinds of Brazilian goods; Chinese boom fueled Brazilian economy and many economists believe, if epicentre of economic crisis was in China, not in Europe, the consequences for Brazil would be much more noticeable. Simply because the European Union is not important as¬† market (20% of Brazilian exports), but it is more important as ¬†source of investments. In this respect, Brazil may be affected by collateral damage caused by the deepening of crisis in eurozone and associated reluctance of global investors to take risks.
First of all because only internal consumption, without  foreign investments,  is not enough to ensure stable growth of  Brazilian economy, especially when economic crisis deepens. Government tries to stimulate internal consumption, decreasing interest rates and taxes, but these measures may not be as effective as 5 years ago. I believe, Brazil has not enough citizens to pay for salvation from crisis. In addition, negative growth of labor force, compared to population growth and rise in labor costs decrease competetiveness of Brazilian companies globally.
In this post I want also to discuss potential problems of relocation to Brazil. Of course, you may say, there are differences such as climate, products and services, language, culture, health care services, etc. And you are aware of all of these differences, actually as anyone decided to move to other country. Yeah, you will feel changes in cuisine, but adaptation period will take not more than 2 weeks and Brazilian food is really nice. As a matter of fact today Brazilian beef is even more popular in such metropolises as Moscow or New York, than is San Paolo.
Punctuality is not about Brazilians. They live in peaceful and relaxed world, maintaining night lifestyle and do not show other than with moonlight. So if you schedule appointment, do not expect people arrive on time, even if they charge you for services. For example if you scheduled house cleaning at 5pm, before you returned from job, people can arrive at 7p.m., when you have family dinner or a bath. However there are still a lot of professionals that are more punctual than the British or Germans. Do not try to schedule anything serious in Siesta hours (just like in Spain) between 12 Noon and 2pm.
Portuguese, French, Hungarian, Russian languages are of the more difficult languages. To learn Portugese you need more than learning . Practice as much as you can, speak wrong, but speak, try
to pick up short expressions, body language and hand gestures.
Altough Brazil is a developing country, cost of living is not extremely lower than in developing countries, if you consider all aspects. Something is cheaper (food, cosmetic procedures and plastic surgeries, insurance, services), something is more expensive (imported goods, communication services, cars, luxury). You can spend 5USD for good quality food in good restaraunt, and double pay for short phonecall to the US.
M.Spivak (MBA) 
- Close to the beach
- In the mountains
- Top choices
- Life in Brazil
- Invest in Brazil
- Why Brazil
- Visa for Brazil
Archives
- January 2024
- April 2019
- February 2016
- December 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- May 2015
- April 2015
- February 2015
- March 2014
- January 2014
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012